Home Insurance
Home insurance is a crucial safeguard for homeowners, offering protection against a variety of risks and unforeseen events that can damage or destroy your home and its contents. Understanding the basics of home insurance can help you choose the right policy to meet your needs and ensure your property is adequately protected.What is Home Insurance?
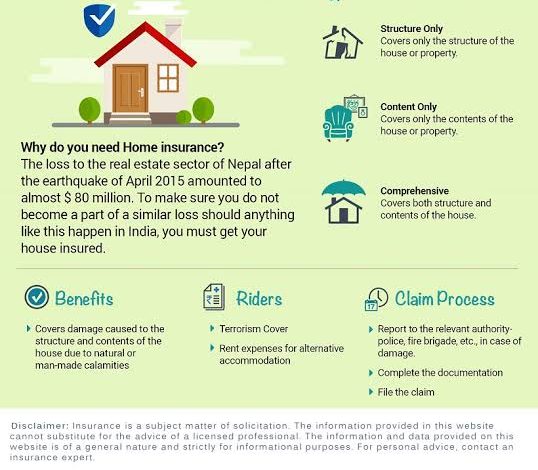
Home insurance, also known as homeowner’s insurance, is a type of property insurance that covers losses and damages to an individual’s house and assets within the home. It typically includes coverage for the following
- Dwelling Protection: This covers the physical structure of the home, including walls, roof, and built-in appliances.
- Personal Property: This covers personal belongings inside the home, such as furniture, electronics, and clothing.
- Liability Protection: This protects against legal claims or lawsuits resulting from injuries or damages that occur on your property.
- Additional Living Expenses (ALE): This covers the cost of living elsewhere if your home is temporarily uninhabitable due to a covered event, such as a fire or severe storm.
Types of Home insurance
- HO-1: Basic coverage for specific perils, such as fire and theft. This type of policy is rare and often considered insufficient.
- HO-2: A broad policy that covers more perils than HO-1, including falling objects and water damage from plumbing.
- HO-3: The most popular policy, providing coverage for all perils except those explicitly excluded, like earthquakes and floods.
- HO-4: Renters insurance, covering personal property and liability for tenants.
- HO-5: Comprehensive coverage, similar to HO-3, but with higher limits and fewer exclusions.
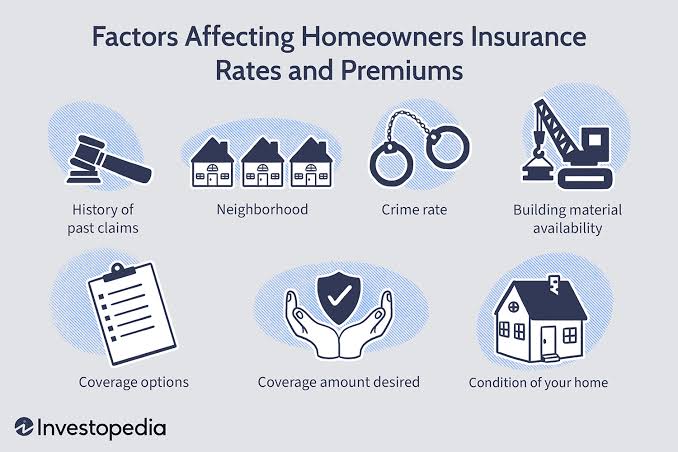
Factor’s affecting Home insurance rates
- Location: Homes in areas prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes or earthquakes, typically have higher premiums.
- Home Characteristics: The age, size, and construction materials of your home can affect your insurance rates.
- Coverage Amount: Higher coverage limits and additional endorsements or riders will increase your premium.
- Deductible: Choosing a higher deductible can lower your premium, but you’ll pay more out-of-pocket in the event of a claim.
- Security Features: Installing security systems, smoke detectors, and fire alarms can reduce your insurance costs.
- Claims History: A history of frequent claims can result in higher premiums.
Tips for Chosing Home Insurance
Assess Your Needs: Determine the value of your home and belongings to ensure you choose adequate coverage.
Compare Quotes: Get quotes from multiple insurance providers to find the best coverage at the most competitive price.
Read the Fine Print: Understand the policy exclusions, limits, and conditions to avoid surprises during a claim.
Bundle Policies: Many insurers offer discounts if you bundle home insurance with other policies, such as auto insurance.
Review Annually: Regularly review and update your policy to ensure it continues to meet your needs and reflects any changes to your home or lifestyle.




